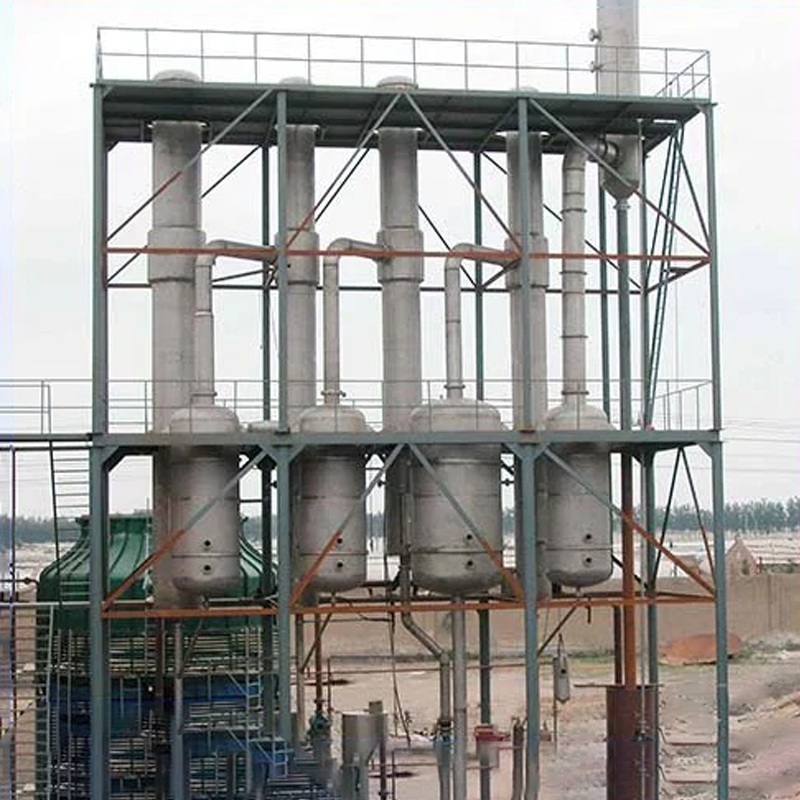
Calcium chloride production lines differ significantly. These variations depend on the output form, either liquid or solid. They also depend on the operation method, whether batch or continuous. Technical specifications further define each type. Every setup is tailored to meet specific industrial needs. Aoliande provides customized, automated solutions. These solutions address worldwide demand. They balance scalability with regulatory adherence and energy savings.
What Are the Main Classifications of Calcium Chloride Production Lines?
Calcium chloride production lines are engineered for different industrial requirements. Their grouping centers on three key aspects. These are the physical form of the final output, the operational approach, and detailed technical specifications. Grasping these differences is vital.
Differentiating Between Liquid and Solid Calcium Chloride Production
The primary way to classify these production lines is by their final product form. Lines making liquid calcium chloride generally involve simpler steps. These steps focus on dissolving starting materials and cleaning the resulting solution. Conversely, lines producing solid calcium chloride need extra stages. These stages include evaporation, crystallization, drying, and granulation. Their purpose is to turn the solution into flakes, pellets, or powder.
Batch vs. Continuous Production Line Systems
Another important difference is the operational method. Batch systems offer more adaptability. This is helpful for smaller operations or making custom blends. However, batch production often becomes less efficient over extended periods. Continuous production setups are built for large-scale output. They deliver consistent quality and experience very little downtime.
Technical Specifications That Define Each Type
Each kind of production line is characterized by specific technical parameters. These include reaction temperature, pressure conditions, evaporation rates, crystallization kinetics, and granulation size control. These details govern the final product’s purity level. They also impact the operational efficiency of the entire setup.
Aoliande supplies both liquid and solid calcium chloride production systems. These systems can operate in batch or continuous mode. They tackle the usual difficulty of balancing process intricacy against cost-effectiveness across different production sizes.
What Are the Core Components of a Calcium Chloride Production Line?
The effectiveness and dependability of a calcium chloride production setup rely heavily on its fundamental parts. Each unit plays a crucial role. They ensure high-quality output while minimizing resource use.
Reactor Systems and Their Functions
Reactor units are central to every calcium chloride production setup. They enable chemical reactions between starting materials. These materials include hydrochloric acid and limestone or calcium hydroxide. The design must support optimal mixing, heat transfer, and reaction kinetics. This ensures complete conversion happens. It also minimizes the formation of unwanted byproducts.
Evaporation and Crystallization Units
In solid calcium chloride production, evaporation units are essential. They concentrate the calcium chloride solution by removing excess water. Multi-effect evaporators are frequently used. They boost energy savings by reusing vapor from one stage to heat the next stage.
Drying and Granulation Equipment
After crystallization, the substance needs drying. Drying achieves the desired moisture level. Rotary dryers or fluidized bed dryers are common. The choice depends on capacity requirements. Granulation equipment follows if pellets or flakes are needed. This includes compactors, pellet mills, or flakers. These machines have sieving mechanisms for controlling size.
Aoliande provides fully combined systems. These systems include reactors, evaporators, crystallizers, dryers, and granulators. They help clients overcome issues linked to part compatibility and process timing within their plants.
Which Raw Materials Are Used Across Various Production Line Types?
The selection of starting substances greatly impacts both process design and final product quality in calcium chloride making. This choice affects chemical yield, equipment wear, environmental measures, and overall running costs.
Common Raw Materials: Limestone, Hydrochloric Acid, and Others
The most frequently used starting substances are limestone, hydrochloric acid, and calcium hydroxide. Sometimes, by-product streams from soda ash plants are used. These streams contain precursors to calcium chloride. The combination depends on availability, expense factors, rules, and the intended product grade. Grades include industrial, food-grade, or pharmaceutical. Hydrochloric acid reacts readily with limestone. This reaction forms a calcium chloride solution and carbon dioxide gas. This simple reaction is favored. However, it requires gas treatment units to manage emissions.
Influence of Raw Material Choice on Final Product Quality
Impurities present in starting substances can significantly affect the final product’s purity. For example, iron oxides in low-grade limestone are problematic. Applications needing very high purity demand refined feedstocks. They also require advanced filtration stages during processing.
Compatibility of Raw Materials with Specific Equipment Designs
Material suitability also extends to equipment selection. For instance, corrosive HCl demands reactors built from corrosion-resistant alloys. Titanium or lined carbon steel tanks with protective coatings are examples. Similarly, abrasive solids like limestone need wear-resistant impellers inside mixing tanks.
Aoliande’s engineering team assesses raw material traits during system planning. This ensures the best reactor setup and material compatibility. It resolves problems related to corrosion resistance or impurity control early in the project.
How Do Different Production Lines Meet Varying Industry Needs?
Calcium chloride serves numerous industries. These range from road upkeep to oil drilling. Each sector needs particular product forms and purity levels. These needs dictate unique line configurations.
High-Purity Industrial Applications
Industries like food processing or pharmaceuticals require extremely pure calcium chloride. It must be free from heavy metals or leftover acids/alkalis. These uses need advanced purification stages. These stages include fine filtration systems, ion-exchange columns, or double-crystallization methods. These steps are integrated into the line design.
Deicing and Road Maintenance Requirements
Municipalities use large amounts of calcium chloride for deicing roads. This is due to its hygroscopic nature. It lowers freezing points effectively, even at very low temperatures. Here, cost-efficiency is more important than high purity. Therefore, continuous solid flake production lines using less expensive feedstocks are ideal.
Oilfield Drilling Fluids and Dust Control Solutions
In oilfields, calcium chloride acts as a brine additive. It enhances fluid density and reduces formation damage during drilling. Similarly, it’s sprayed over unpaved roads for dust control. This works because it retains moisture. Liquid systems making concentrated brines are preferred here. They allow easy transport via tankers directly to field sites. No extra processing is needed onsite.
Aoliande customizes each setup according to end-user needs. It ensures the right balance between capacity, product form, and purity demands. This applies across diverse sectors, from city deicing projects to offshore drilling platforms.
How Do Traditional and Modern Production Lines Compare?
Technology has evolved. It moved from manually operated batch plants to highly automated continuous facilities. Modern plants offer better efficiency across key indicators. These include yield rates, energy use, labor intensity, and environmental impact.
Key Differences in Process Efficiency
Modern plants use real-time sensors connected through PLC/DCS platforms. These enable adjustments during the process. This minimizes waste and maximizes conversion per input tonnage. Legacy analog setups are more prone to errors. Human intervention delays or mistakes during operations are the cause.
Advancements in Automation and Control Systems
Automation improves consistency. It also enhances safety through remote monitoring. Operators intervene only when necessary. This reduces exposure risks, especially when handling corrosive reagents like HCl under pressure. SCADA integration allows centralized control over multiple lines. This is true even across large facilities. It significantly reduces manpower over time. This sustainably lowers operating expenses.
Energy Consumption and Environmental Considerations
Multi-effect evaporators are now standard. They drastically cut steam demand compared to older single-stage designs. Closed-loop cooling circuits greatly limit water waste. This is a major improvement over open-loop systems common decades ago.
Aoliande incorporates modern automation into its newest plants. It helps clients transition smoothly from old setups. The goal is greener, more efficient operations aligned with ESG goals mandated globally.
What Role Does Customization Play in Choosing a Production Line?
No two clients have identical requirements. Off-the-shelf solutions often fail to achieve ROI targets. Specific market contexts vary. Factors include feedstock availability, rules, and plant layouts.
Tailoring Capacity to Operational Scale
Smaller firms may need compact skid-mounted units. These produce a few tons per day. Large corporations seek modular, expandable setups. These can handle 100+ tons per day. They integrate smoothly with existing ERP/MES platforms for managing supply chains.
Regional Compliance and Safety Standards
Local regulations often set emission limits, noise levels, and effluent discharge norms. This necessitates including scrubbers, silencers, or neutralization pits. Addressing this during engineering is better than costly retrofitting later. Certifications like ISO9001, CE marking, and ATEX compliance are mandatory in certain regions. This is especially true in the EU and Middle East. It’s critical when handling hazardous chemicals in enclosed areas with explosion risks.
Integration with Existing Plant Infrastructure
Adding a new line to an existing site poses challenges. These include space, utility access, and automation interfacing. These are manageable if the vendor understands the client’s current setup thoroughly. Detailed site surveys and P&ID reviews are necessary.
Aoliande excels at delivering complete customized solutions. These are tailored not just to technical specs but also to real operator constraints. This ensures smooth commissioning and minimal disruption.
Why Is Aoliande Chemical Equipment a Trusted Supplier in This Field?

As demand for dependable calcium chloride technology grows globally, reliable partners become invaluable. They ensure project success within set timelines and budgets.
Overview of Aoliande’s Product Range for Calcium Chloride Production
Aoliande offers full sets of equipment. These include reactors, evaporators, dryers, granulators, and packaging machines. They are tailored for both liquid and solid outputs. They cover batch and continuous operation modes. Whether a client needs a compact pilot plant for R&D or a large commercial installation, Aoliande provides scalable, modular setups. These adapt to future expansions easily.
Engineering Expertise and After-Sales Support
Decades of chemical process engineering experience back Aoliande. They assist clients at every stage. This includes feasibility analysis, layout optimization, procurement, logistics, commissioning, and training. Preventive maintenance and service contracts are part of post-handover support. Robust documentation packages back all projects. These cover PFDs, P&IDs, electrical schematics, operator manuals, SOPs, and spare parts lists. This facilitates a smooth handover to local teams.
Global Installations and Proven Track Record
References span continents—Asia, Africa, Europe, and the Americas. Industries served include municipal utilities, mining firms, petrochemical giants, and specialty chemical makers. Clients consistently cite reliability, responsiveness, and professionalism as hallmarks of working with Aoliande long-term.
Conclusion
Choosing among the various calcium chloride production lines requires understanding your operational needs. Consider the desired output form (liquid/solid) and the scale (batch/continuous). Consider locally available starting materials too. Align these factors against the technical capabilities offered by suppliers. Aoliande combines engineering skill, customization flexibility, and worldwide experience. They deliver dependable solutions repeatedly.
FAQs About Calcium Chloride Production Lines
What is the typical lifespan of a calcium chloride production line?
Properly maintained systems typically last 15 to 20 years. Actual duration depends on usage intensity and operating conditions.
Can a production line be modified to switch between liquid and solid calcium chloride outputs?
Yes, modification is possible. However, it requires a modular design planned from the start. This allows bypassing or adding stages like evaporation, drying, or granulation as needed for future changes.
What certifications should a reliable calcium chloride production line comply with?
Important certifications include ISO9001 and CE marking. ATEX compliance is necessary depending on the region and specific rules. Industries like food or pharma additionally require adherence to GMP/HACCP standards.