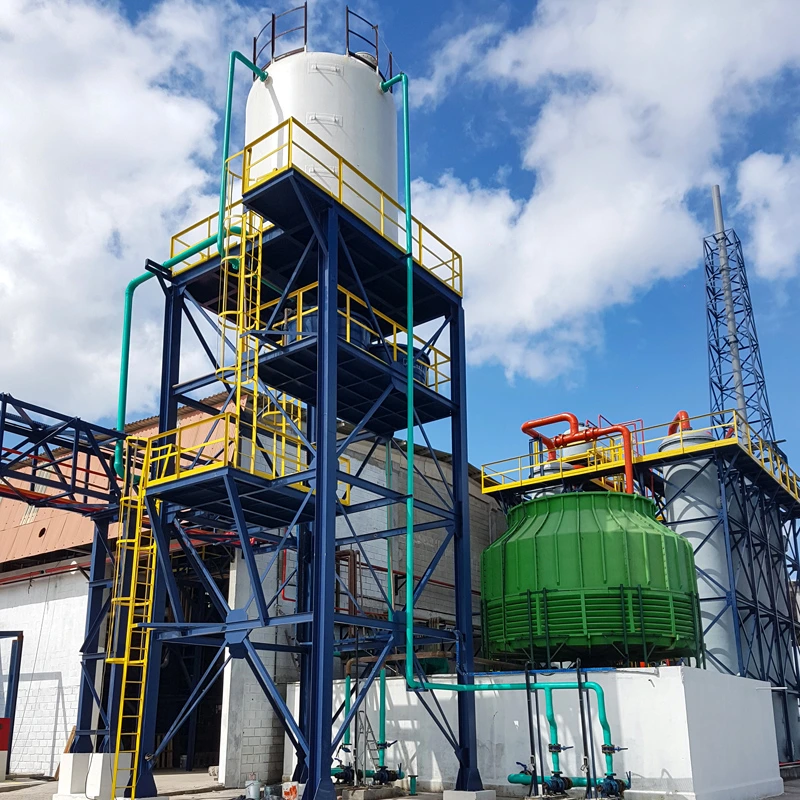
The Basics of Sodium Sulfate Production
Key Raw Materials Used in the Production Process
To produce sodium sulfate, you first pick the right raw materials. The main ones are sodium chloride, table salt, and sulfuric acid. These are key for the chemical reactions that make sodium sulfate. In factories, the quality of these materials affects how well the process goes and what you get in the end. Good plants, like those from Aoliande, handle these materials carefully to get top results.
The Chemical Reaction Behind Sodium Sulfate Formation
Sodium sulfate comes from a chemical reaction. You combine sodium chloride with sulfuric acid under certain conditions. This takes place in special equipment at high heat. The result is sodium sulfate, with hydrogen chloride as a byproduct. The reaction is: 2 NaCl + H2SO4 → Na2SO4 + 2 HCl
You have to keep the temperature just right. Good systems for moving materials help the reaction finish and save energy. Aoliande uses smart tech, like better furnace flues, to use less energy.
Historical Context of Sodium Sulfate Manufacturing
People began making sodium sulfate years ago. It started with uses in glass making and detergents. Over time, new tools made the process better. Old, simple setups turned into modern factories. Aoliande helped with this change. They brought in machines that work well and help the environment.
Industrial Methods for Producing Sodium Sulfate
The Mannheim Process and Its Applications
The Mannheim process is a popular way to make sodium sulfate. You mix sodium chloride and sulfuric acid in a muffle furnace. It gets hotter than 600°C. This makes sodium sulfate and hydrochloric acid. The acid can be reused or used in other ways.
Aoliande makes machines for this process. Their equipment has parts that don’t rust and systems to catch hydrochloric acid. Automatic controls keep things running smoothly and follow environmental rules.
The Role of the Hargreaves Process in Modern Production
There’s also the Hargreaves process. It uses sulfur dioxide, oxygen, water, and sodium chloride to make sodium sulfate. This way costs less and is kinder to the environment than older methods. It’s not used as much as the Mannheim process but works for some jobs.
Alternative Methods and Their Efficiency
You can also find sodium sulfate in natural deposits, like mirabilite or Glauber’s salt. These methods use less energy but depend on where the deposits are. Man-made processes, like those from Aoliande, give steady quality and can grow big. This makes them great for the industry.
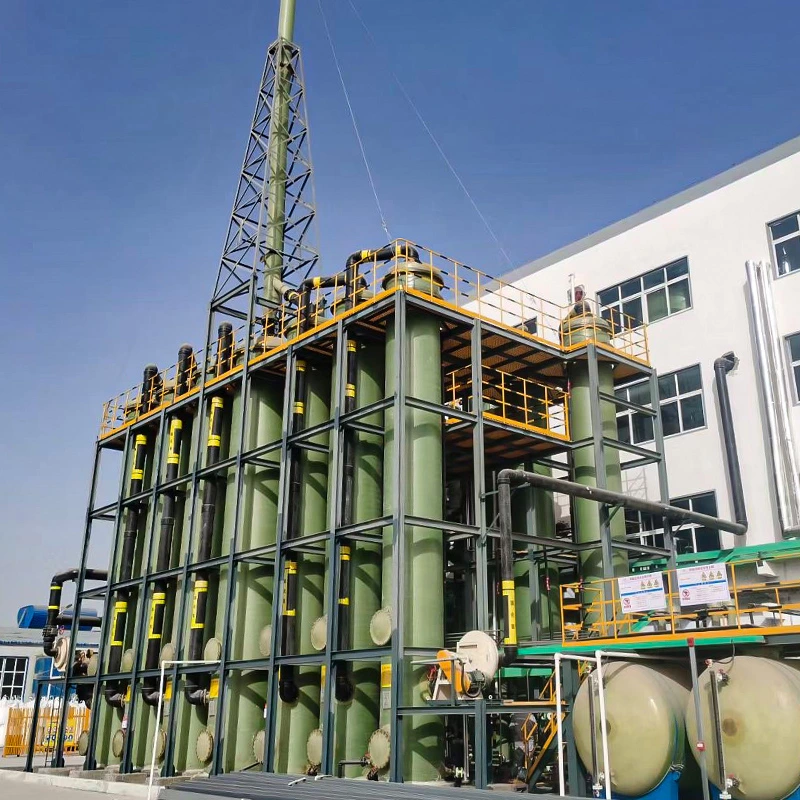

Applications of Sodium Sulfate in Various Industries
Use in Detergents and Cleaning Agents
Sodium sulfate is used a lot in detergents. It acts as a filler to improve texture and how it dissolves. It also keeps costs down. Since it’s not toxic, it’s safe for home cleaners.
Importance in Glass Manufacturing
In glass making, sodium sulfate is a fluxing agent. It clears out tiny air bubbles in melted glass. This makes the glass clear and even.
Role in Paper and Textile Industries
The paper industry uses sodium sulfate in kraft pulping. It helps recover chemicals for making paper. In textiles, it help with dyeing by making colors spread evenly on fabrics.
Environmental Considerations in Sodium Sulfate Production
Waste Management Practices in the Industry
Making sodium sulfate creates waste. You need to handle it carefully. Hydrochloric acid from the Mannheim process is a big issue. Modern plants have systems to recycle this acid. This follows environmental rules and cuts waste. It also saves money for the plants.
Energy is a concern too. High-heat reactions, like in the Mannheim process, need lots of energy. Aoliande improved furnace designs. Their new flues heat evenly, finish reactions, and save energy.
Reducing Environmental Impact Through Sustainable Techniques
The industry is finding ways to be greener. One way is using better materials for machines. Aoliande uses parts that don’t rust. This makes machines last longer and cuts waste from fixes.
Modern plants use automatic systems too. These control how much material is used to avoid waste. By adjusting amounts carefully, they keep quality steady and use less extra. Aoliande’s PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) systems show how automation helps with green goals.
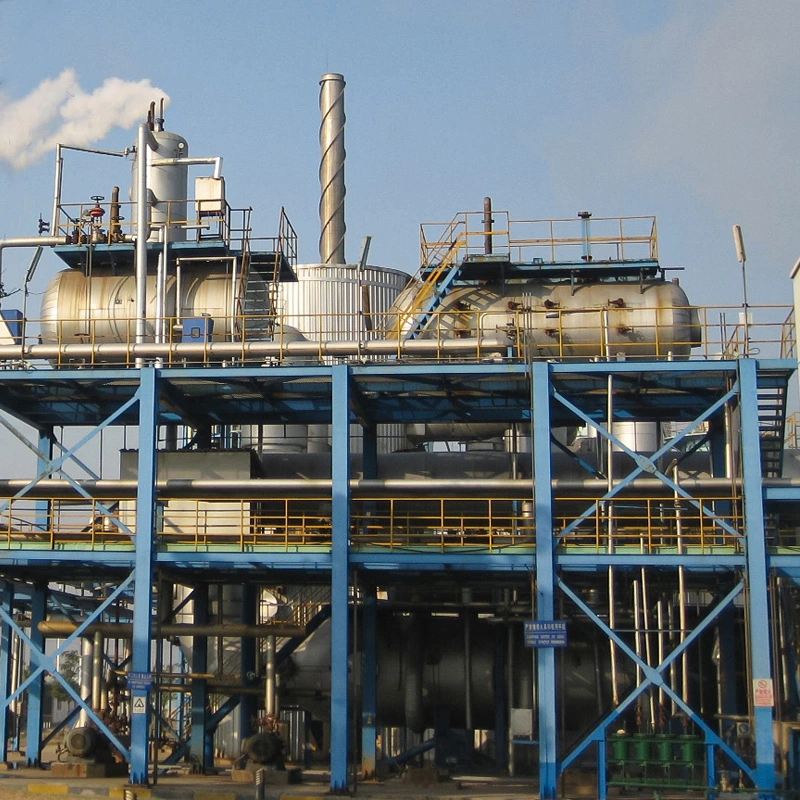

Aoliande: A Leading Name in Chemical Solutions
Overview of Aoliande’s Contribution to Sodium Sulfate Production
Aoliande is a big name in sodium sulfate production. They make Mannheim process production lines. Their solutions focus on working well and being eco-friendly. They keep improving their machines to stay ahead.
Aoliande does more than build machines. They offer advice, improve designs, handle transport, and help with setup. This full support helps clients with sodium sulfate production.
Exploring Aoliande’s Diverse Range of Chemical Products
Aoliande makes more than sodium sulfate equipment. Our offer Hydroxypropyl Methylcellulose Production Lines, Calcium Chloride Production Lines, and Water Soluble Fertilizer Production Lines. We also make FRP (Fiber Reinforced Plastic) machines, like filament winding and molded grating machines.
Each product shows its focus on quality and new ideas. Our FRP products are strong and useful for many things. They’re used in seawater desalination, power plant desulfurization, and city water systems. This shows Aoliande can solve many industry problems.
For inquiries about our cutting-edge sodium sulfate production line solutions:
WhatApp: +86-13363884492 Email: belen@aldfrp.com.
FAQ
Q: What are the main raw materials required for sodium sulfate production?
A: Sodium chloride (table salt) and sulfuric acid are the primary raw materials used.
Q: How does the Mannheim process produce sodium sulfate?
A: It involves reacting sodium chloride with sulfuric acid at high temperatures to produce sodium sulfate and hydrochloric acid.
Q: What industries use sodium sulfate extensively?
A: It is widely used in detergents, glass manufacturing, paper production, and textile dyeing.
Q: What makes Aoliande’s equipment stand out?
A: Their equipment features corrosion-resistant materials, advanced designs for energy efficiency, automated controls, and robust environmental compliance measures.
Q: Are there alternative methods to produce sodium sulfate besides synthetic processes?
A: Yes, natural extraction from mineral deposits like mirabilite is an alternative method but depends on geographical availability.